Introduction What Is Sequence Weight Loss: Sequence weight loss, also called progressive weight loss, is a structured approach to sustainable, long-term weight management. Unlike crash diets or quick-fix solutions, sequence weight loss emphasizes gradual and steady progress towards a health body weight and lifestyle. This method emphasizes sustainable habits for weight loss and overall well-being, not just shedding pounds. The concept of sequence weight loss emphasizes small, consistent changes for significant, lasting results in diet, exercise, and habits. This approach sets incremental weight loss goals, emphasizing achievable milestones and increasing effort gradually with progress. Sequence weight loss takes into account the importance of patience, self-discipline, and a holistic view of health. Exploring its benefits and distinctions from drastic weight loss, shedding light on its preference for healthier, sustainable weight management. Sequence weight loss is a method that recognizes the challenges and complexities of achieving and maintaining a healthy weight in today’s fast-paced world. It is a departure from the often unsustainable, crash dieting trends that promise quick results but rarely deliver lasting change. Instead, sequence weight loss encourages individuals to …
Weight Loss Challenges
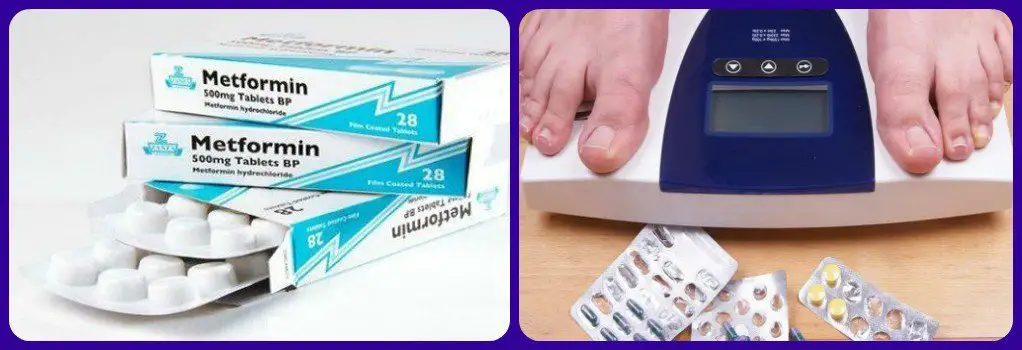
Introduction Metformin has long been a cornerstone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, and it is often prescribed off-label for weight loss. However, as medical research and understanding of weight management continue to evolve, the quest for more effective alternatives to Metformin has intensified. Weight management is a complex interplay of genetics, lifestyle, and metabolic factors, and while Metformin may yield positive outcomes for some individuals, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. This quest for a better approach to weight loss is driven by a desire to find methods that are not only effective but also sustainable and safe. Obesity and excess weight are significant health concerns worldwide, contributing to various chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension. Therefore, the search for alternatives to Metformin is fueled by the urgency to combat the obesity epidemic and its associated health risks.In this exploration, we will delve into the current landscape of weight loss strategies and explore options that may offer promising alternatives to Metformin, considering both pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical approaches. It is essential to remember that individual responses …
Introduction In a world where health and well-being have become paramount, the journey towards achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is a pursuit that touches the lives of millions. Able Weight Loss, a comprehensive and personalized approach to shedding excess pounds and embracing a healthier lifestyle, has emerged as a beacon of hope for those seeking sustainable weight management solutions. This innovative program transcends the fads and quick fixes that saturate the weight loss industry, offering a science-based, holistic, and individualized approach to help individuals reach their fitness goals. Able Weight Loss is not just about shedding pounds; it’s about empowering individuals to take control of their lives, make informed choices, and foster lasting habits that lead to a happier, healthier existence. By blending nutrition science, physical activity, behavior modification, and mental wellness, Able Weight Loss equips individuals with the knowledge, tools, and support needed to embark on a transformative journey towards improved health and vitality. In this exploration of Able Weight Loss, we will delve into the core principles, methodologies, and success stories that define this program, illuminating the …
Introduction How Effective Is Pilates For Weight Loss: Pilates, unlike traditional high-intensity workouts, is renowned for its emphasis on core strength, flexibility, and controlled movements. At first glance, it may not seem like an obvious choice for those seeking weight loss. However, the true power of Pilates lies in its ability to address the fundamental aspects of fitness that are often overlooked in more conventional exercise routines. By targeting core muscles, improving posture, and enhancing overall body awareness, Pilates sets the stage for sustainable and long-term weight management. One of the key factors contributing to Pilates’ effectiveness in weight loss is its adaptability to various fitness levels and needs. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned athlete, Pilates can be tailored to suit your unique requirements. It provides a low-impact workout that is gentle on the joints, making it accessible to individuals of all ages and fitness backgrounds. The versatility of Pilates equipment, such as the reformer and Cadillac, allows for progressive resistance training, enabling users to gradually increase the intensity of their workouts as their fitness levels improve. …
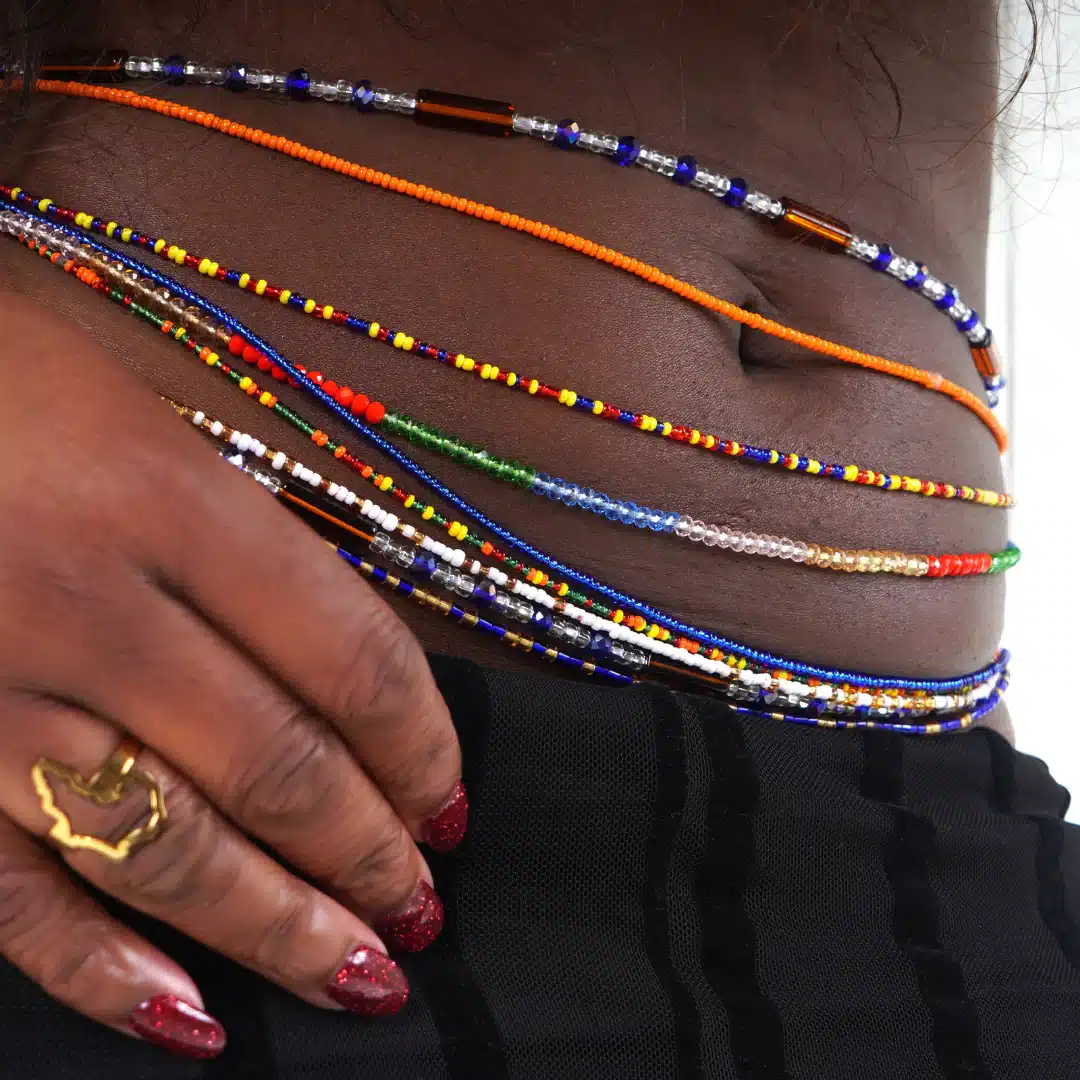
Introduction What Are Waist Beads For Weight Loss: Waist beads, also known as “girdles” or “belly beads,” are typically made of various materials, such as glass, ceramic, plastic, or semi-precious stones, and are strung together on a string or wire. They come in an array of colors, patterns, and designs, making them a versatile and customizable accessory. While they are appreciated for their aesthetic appeal, they are believed to offer additional benefits when it comes to weight loss. One of the key aspects of waist beads for weight loss is the mindfulness they promote. Wearing these beads around the waist provides wearers with a tangible and visual reminder of their fitness goals and body size. By tracking changes in the fit and positioning of the beads, individuals can become more aware of their body’s changes and make informed decisions about their diet and exercise routine. Waist beads can also serve as a form of motivation and encouragement. As wearers embark on their weight loss journey, the gradual movement of the beads towards a tighter fit can be incredibly satisfying and …
Introduction What Are Snaps For Weight Loss: Snaps, in the context of weight loss, refer to a range of snack choices that are strategically curated to support the goals of calorie control, portion management, and nutrient density. These snacks offer a smart and convenient way to bridge the gap between meals, curb cravings, and ensure that the body remains adequately fueled throughout the day. Unlike traditional, calorie-laden snacks that can thwart weight loss efforts, snaps are designed to provide maximum nutritional benefit with minimal caloric intake. The concept of snaps encompasses a diverse array of foods, from fresh fruits and vegetables to lean protein sources and whole grains. Their key characteristic is their ability to satisfy hunger while delivering essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and protein. As such, they help individuals strike a harmonious balance between fulfilling their cravings and adhering to a calorie-controlled diet – a crucial aspect of any sustainable weight loss plan. Aims to explore the underlying principles and benefits of incorporating snaps into your weight loss journey. We will delve into the science behind these snacks, how …
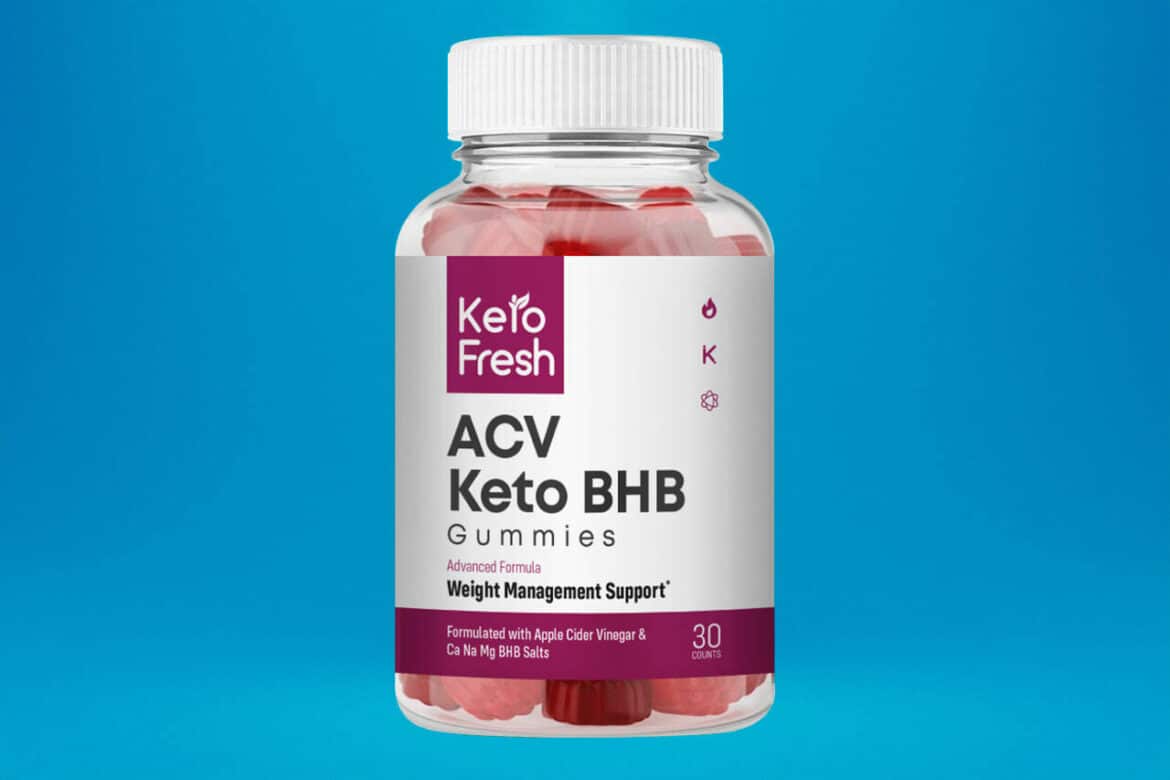
Introduction What Are The Best Keto Acv Gummies For Weight Loss: The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the “keto” diet, has gained immense traction due to its ability to induce a state of ketosis in the body, where it primarily burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This metabolic shift has been associated with significant weight loss and improved overall health for many individuals. Meanwhile, apple cider vinegar has a longstanding reputation for its potential health benefits, including aiding in digestion and helping to control blood sugar levels. Keto ACV gummies combine the power of both ketogenic principles and apple cider vinegar into one convenient and palatable package. These gummies typically contain a blend of key ingredients, including exogenous ketones, MCT oil, and, of course, apple cider vinegar. Exogenous ketones can help support ketosis, while MCT oil provides a quick and efficient source of energy for those following the keto diet. The ACV is believed to enhance the gummies’ potential to assist with weight loss by promoting feelings of fullness and supporting healthy digestion. While the idea of consuming …
Introduction What Are The Side Effects Of Weight Loss Gummies: Weight loss gummies typically contain a combination of ingredients that are believed to support weight loss, such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, and herbal extracts. While many of these components can be beneficial when used in moderation, the concentrated form found in gummies can lead to various side effects. One of the primary concerns associated with weight loss gummies is their potential to cause gastrointestinal discomfort. The high concentration of certain ingredients, such as fiber and sugar alcohols like sorbitol or xylitol, can lead to digestive issues like gas, bloating, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. These side effects can be particularly bothersome for individuals with sensitive stomachs or those who consume excessive amounts of gummies in pursuit of rapid weight loss. The excessive consumption of weight loss gummies can lead to adverse effects on blood sugar levels. Many of these gummies contain added sugars or sweeteners, which can cause spikes and crashes in blood sugar, leading to mood swings, energy fluctuations, and cravings for more sugary foods. It’s also essential to consider …
Introduction Does Olive Oil Help With Weight Loss: Olive oil, a staple of Mediterranean cuisine, has garnered a reputation not only for its rich flavor but also for its numerous health benefits. Its unique composition, primarily consisting of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), particularly oleic acid, sets it apart from other cooking oils. These MUFAs are believed to play a pivotal role in various aspects of health, including weight management. The premise behind the potential weight loss benefits of olive oil lies in its ability to influence several mechanisms within the body. Firstly, MUFAs are known to promote satiety and reduce appetite, which may lead to lower calorie consumption over time. Additionally, these healthy fats may enhance the thermogenic effect of food, meaning they could slightly boost the body’s calorie-burning capacity after a meal. Olive oil is rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, which may indirectly support weight loss by reducing chronic inflammation and metabolic disturbances often associated with obesity. While these potential mechanisms paint an intriguing picture, Navigate this subject with a critical lens. Scientific research on olive oil’s direct …
Introduction How Many Walnuts A Day For Weight Loss: Walnuts are a nutrient-dense nut, packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, making them a popular choice among health-conscious individuals. Their unique nutritional profile, highlighted by omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein, has led researchers and nutritionists to explore their potential as a weight loss aid. However, determining the optimal daily intake of walnuts for weight loss is not a one-size-fits-all proposition and involves a nuanced understanding of individual goals, dietary preferences, and overall caloric intake. We will delve into the science behind walnuts as a potential tool for weight management. We will examine the nutritional composition of walnuts, their impact on appetite control, metabolism, and satiety, and discuss how they fit into various dietary approaches, such as low-carb, Mediterranean, or vegan diets. Moreover, we will address the potential pitfalls of consuming too many walnuts, such as excessive calorie intake, and provide practical guidelines to help you make informed decisions about integrating them into your daily diet for weight loss. As we navigate this complex terrain of walnuts and weight …