Introduction
What Does A Torn Tricep Look Like: A torn triceps, also known as a triceps tendon tear, is a significant injury that can cause pain, weakness, and limited mobility in the arm. The triceps muscle is located on the back of the upper arm and is responsible for extending the elbow joint. When the triceps tendon, which connects the muscle to the bone, becomes torn or ruptured, it can have a noticeable impact on the appearance and function of the affected arm.
What a torn triceps looks like can vary depending on the severity of the injury. In less severe cases, a partial tear may not result in a noticeable change in the arm appearance. One of the first noticeable signs of a torn triceps is swelling around the elbow region and the back of the upper arm. The affected area may appear larger or more swollen compared to the uninjured arm. This weakness can be a clear indicator of the injury.
A torn triceps can cause bruising, which may be extensive and extend down the arm. The bruising is typically a result of bleeding into the tissues surrounding the injury. In some cases, a complete triceps tendon tear can lead to a visible deformity in the arm. This may manifest as a noticeable gap or depression in the muscle near the elbow. A torn triceps will result in significant weakness in the affected arm, particularly when trying to straighten the elbow or perform pushing movements.
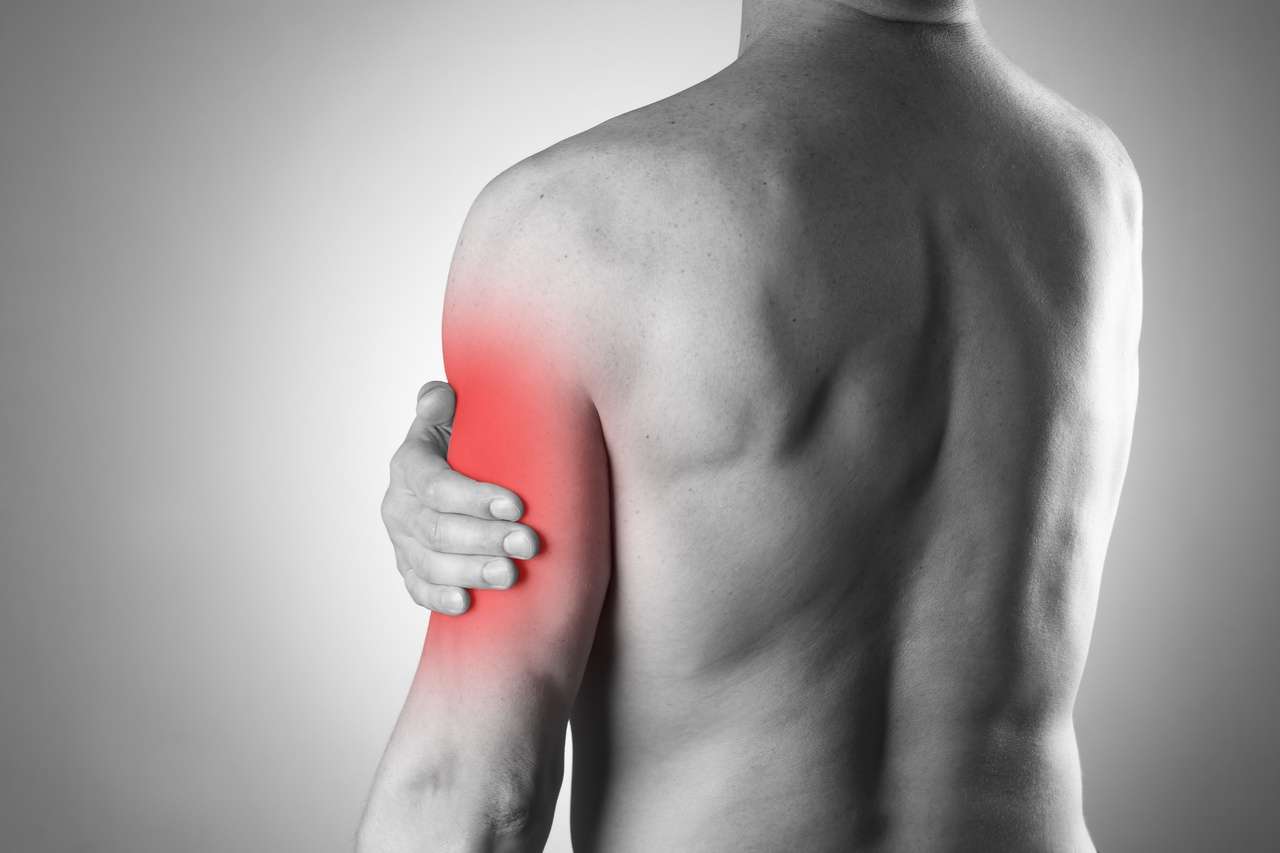
How do you know if you tore your tricep?
Triceps tears cause immediate pain in the back of your elbow and upper arm that worsens if you try to move your elbow. You might also feel (or hear) a popping or tearing sensation. You will have swelling, and your skin will likely be red and/or bruised.
If you believe you’ve suffered a tricep injury, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are some signs and symptoms that may indicate a tricep tear:
Sudden, Sharp Pain: A torn tricep often causes a sharp, intense pain at the time of injury. This pain may subside to some extent afterward but typically persists.
Swelling and Bruising: Swelling around the injured area is a common sign. You might notice immediate or delayed bruising, indicating internal bleeding.
Weakness and Limited Mobility: A tricep tear can lead to significant weakness in the arm, making it challenging to perform simple tasks like lifting objects or extending the elbow. You may also experience limited range of motion.
Popping Sensation: Some individuals report hearing or feeling a popping sensation when the injury occurs.
Visible Deformity: In severe cases, a visible deformity in the arm may be noticeable, where the tricep muscle appears bunched up or out of place.
Tenderness to Touch: The injured area may be tender and painful to touch, indicating the location of the tear.
Muscle Contractions: Attempting to contract the tricep muscle can be painful or impossible, further confirming the injury.
Numbness or Tingling: In rare cases, nerve involvement can lead to numbness or tingling sensations in the affected arm.
Will a torn tricep heal itself?
Depending on the severity of the damage, a triceps tendon injury may heal on its own or require surgery to repair it: Nonsurgical treatment includes resting the elbow and limiting the number of repetitive motions. Applying ice every 20 minutes for a few hours can help reduce triceps irritation and pain.
A torn tricep will not heal itself completely without proper medical intervention. While the body has a natural ability to repair damaged tissues, including muscles, a significant tricep tear requires medical evaluation and often surgical intervention for the best outcomes.
When a tricep muscle is torn, the muscle fibers can separate, leading to pain, weakness, and limited function. In some minor cases, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) may help alleviate symptoms, and the muscle may heal to some extent. In more severe tears, the muscle may not heal effectively on its own, and untreated injuries can lead to long-term issues such as chronic weakness, decreased range of motion, and the risk of re-tearing.
Medical assessment is crucial to determine the extent of the tear. Treatment options may include surgery to reattach the torn muscle fibers, followed by a comprehensive rehabilitation program to regain strength and function. Physical therapy plays a vital role in the recovery process.
Ignoring a torn tricep or attempting to heal it solely through rest and self-care measures is not advisable, as it may result in suboptimal healing and persistent functional limitations. Seeking prompt medical attention and treatment plan is essential to ensure the best chance of a full recovery and restored arm function.
Can you workout with a torn tricep?
With minor tears you may be able to continue activities or sport with minimal restriction. The pain and tightness may gradually increase following the exercise as bleeding and swelling occurs around the injured muscle.
Exercising with a torn tricep is especially without proper medical guidance. A torn tricep is a serious injury that can significantly impair arm function and lead to further complications if not managed correctly.
Continuing to work out with a torn tricep can worsen the injury, increase pain, and hinder the healing process. The tricep muscle plays a crucial role in various upper-body movements, and any stress placed on it during exercise can disrupt the healing tissues, potentially leading to a more severe tear or complications.
The initial treatment for a torn tricep typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and swelling. Once a diagnosis is confirmed, your healthcare provider will prescribe a tailored treatment plan, which may include surgery and physical therapy.
Your healthcare provider’s advice and refrain from strenuous physical activity until you receive clearance. Attempting to work out with a torn tricep can also increase the risk of compensatory movements that put additional strain on other muscles and joints, potentially leading to imbalances and secondary injuries.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for proper assessment, treatment, and guidance on when and how to safely return to exercise after a torn tricep injury. Prioritizing your long-term health and recovery is crucial in such cases.
How long does a pulled tricep muscle take to heal?
The back of your arm may be sensitive to the touch and hurt when pressure is applied. In more severe cases (Grade 2 and 3) there can be visible bruising and even a ‘ridge’ or ‘break’ in the muscle depending on the extent of the tear. The more severe cases may take up to 12 weeks to completely heal.
The healing time for a pulled tricep muscle can vary significantly depending on the severity of the injury, individual factors, and the effectiveness of the treatment and rehabilitation. Mild to moderate tricep strains or pulls may take several weeks to heal, while more severe tears may require several months or longer.
Acute Phase (1-2 weeks): During the initial phase, the focus is on reducing pain and inflammation. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are often. Immobilizing the affected arm with a brace or sling may also be necessary.
Recovery Phase (2-6 weeks): As the acute symptoms subside, you can begin gentle range-of-motion exercises and possibly start physical therapy. The goal is to regain mobility and prevent muscle atrophy.
Strengthening Phase (6-12 weeks): Once pain is well-managed, you can gradually introduce strength-building exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist. This phase is crucial for rebuilding muscle strength.
Return to Activity (2-3 months or more): Depending on the extent of the injury and your progress, you may gradually return to your normal activities, including sports or regular workouts. Full recovery can take several months, especially for severe tears.
Not rush the healing process to prevent re-injury. Pushing too hard or returning to strenuous activities too soon can prolong recovery and increase the risk of complications.
Do tricep tears need surgery?
Most complete triceps tendon ruptures require repair otherwise there will be a significant loss of extension strength. Full tears should be repaired within 2 to 3 weeks of injury otherwise these may need to be augmented with a graft to obtain a complete repair.
The need for surgery to repair a tricep tear depends on the severity and location of the injury. Not all tricep tears require surgical intervention, but some do.
Location of the Tear: Tricep tears can occur at various locations along the muscle-tendon unit. Tears closer to the tendon’s attachment point on the elbow are more likely to require surgery, as they can significantly affect arm function.
Severity of the Tear: Partial tears or strains may heal with conservative treatment, such as rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. Complete tears or severe tears that significantly impair arm function often require surgery.
Patient’s Activity Level: The patient’s activity level and functional demands play a role in the decision. Athletes or individuals who require a high level of arm function may be more likely candidates for surgery to optimize recovery.
Failure of Conservative Treatment: If conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief or if the tricep tear fails to heal correctly, surgery may become necessary.
Timing: In some cases, the timing of surgery can be a critical factor. Early intervention may be more effective in achieving better outcomes, for complete tears.
Surgery involves reattaching the torn tricep tendon or muscle fibers to their original attachment point. After surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is essential to regain strength, mobility, and function gradually.
How rare is a tricep tear?
Triceps tendon tear is a relatively rare injury and the rupture of the distal triceps is the most uncommon rupture in the upper extremity (less than 1% of all the upper extremity tendon injuries).
The triceps brachii muscle is a robust muscle located on the back of the upper arm, responsible for extending the elbow joint. Unlike some other muscles that are more prone to tears, the triceps is a thick, powerful muscle with strong tendinous attachments. It is less susceptible to acute tears during regular daily activities or even during most workouts.
Sports Injuries: Trauma during high-impact sports, particularly those involving weightlifting, bodybuilding, or heavy resistance training, can occasionally lead to tricep tears.
Accidents: Traumatic accidents, such as falls or motor vehicle accidents, can cause tricep tears, but these are relatively rare.
Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Overuse injuries in the triceps, such as tendinopathy or chronic strains, are more common than acute tears.
Tricep tears are not as common as some other muscle injuries, they do require proper medical evaluation and care when they occur. It’s essential to seek medical attention if you suspect a tricep injury to determine the extent of the damage and receive appropriate treatment.
How long does tricep pain last?
Treatment should include rest initially along with icing. When the pain is tolerable, light movement and stretching will help avoid stiffness. If pain is extreme and intolerable or lasts more than 1 to 2 weeks after the injury, you should call your doctor.
The duration of tricep pain can vary widely depending on the cause, severity, and individual factors. Tricep pain may last for a short period or become a chronic issue.
Acute Injury: If the tricep pain is due to a recent injury, such as a strain or tear, acute pain can last for a few days to a few weeks. The acute phase is typically characterized by significant discomfort, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Overuse or Strain: Tricep pain resulting from overuse or strain may persist for several weeks to a few months. Rest, anti-inflammatory measures, and appropriate rehabilitation exercises can help alleviate pain and promote healing.
Chronic Conditions: In cases of chronic conditions like tendinopathy or tendinitis, tricep pain can persist for several months or even become a long-term issue. Chronic pain often requires ongoing management, including physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and possibly corticosteroid injections or other treatments.
Medical Conditions: Tricep pain stemming from medical conditions like arthritis or nerve compression may last for an extended period, potentially becoming a recurring or chronic problem.
How do you fix a tricep injury?
Application of ice and heat to reduce swelling and pain. Prolonged rest to the injured triceps muscle to promote healing. Use of compression straps around the triceps muscle to reduce discomfort. Physical therapy and exercise regimen to improve range of motion and strengthen muscles.
Seek Medical Evaluation
If you suspect a significant tricep injury, such as a tear or rupture, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform a thorough examination, potentially including imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans, to determine the extent of the injury.
Rest and Immobilization
Rest is essential for the healing process. Depending on the severity of the injury, your healthcare provider may recommend immobilizing the affected arm with a splint or brace. This prevents further strain on the tricep muscle and promotes healing.
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may be recommended to manage pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medication.
Physical Therapy
Once the acute phase of the injury has passed, physical therapy is often prescribed. A skilled physical therapist can create a customized rehabilitation program to strengthen the triceps, improve flexibility, and restore function. Exercises may include gentle stretching, range of motion exercises, and progressive resistance training.
Gradual Return to Activity
Returning to activities that involve the triceps should be gradual g by your healthcare provider or physical therapist. Rushing back into strenuous activities too soon can lead to reinjury.
Conclusion
A torn triceps, or triceps tendon tear, is a potentially serious injury that can have a range of visual and functional manifestations. The appearance of a torn triceps can vary depending on the severity of the injury and individual factors, but there are common signs and characteristics to be aware of. One of the hallmark signs of a torn triceps is swelling around the elbow area and the back of the upper arm.
This swelling occurs as a result of the body’s natural response to injury, where fluids accumulate in the affected area. Alongside swelling, extensive bruising often accompanies a torn triceps, which can extend down the arm. The bruising is a consequence of bleeding into the surrounding tissues and serves as a clear indicator of injury. A complete triceps tendon tear may lead to a visible deformity in the arm.
This can manifest as a noticeable gap or depression in the muscle near the elbow, suggesting a loss of continuity in the triceps tendon. Individuals with a torn triceps commonly experience significant weakness in the affected arm, particularly when attempting movements that engage the triceps muscle, such as straightening the elbow or pushing against resistance. This weakness can significantly impact daily activities.


1 comment
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here to that Topic: thefitnessblogger.com/what-does-a-torn-tricep-look-like/ […]